World Eye Donation Day: Nelson Hospital’s First Eye Implant Surgery
World Eye Donation Day: Nelson Hospital’s First Eye Implant Surgery…
9518951959
info@nelsonhospitals.com
9518951959

Women typically experience menstrual cycles from the age of 11–12 years until around 50 years. During this 35–40 year span, it is not unusual to have a few episodes of bleeding that don’t follow the normal pattern. However, if this irregularity continues or becomes frequent, it should not be ignored. Consulting a gynecologist becomes important.
Abnormal uterine bleeding may include an increase in the number of bleeding days, heavy bleeding with clots, associated abdominal pain, or unpredictable, irregular bleeding. Normally, menstrual bleeding lasts up to 7 days. Any bleeding that is longer, heavier, or happens outside the usual cycle is considered abnormal and may need medical attention.
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding (AUB) refers to any type of bleeding from the uterus that is unusual in its timing, amount, or duration. It is different from your regular monthly period. This condition can occur in women of any age — from adolescence to menopause — and may affect your daily life, health, and emotional well-being.
Bleeding is considered abnormal if:
This condition is also known by other names such as:
Abnormal uterine bleeding is not just a physical inconvenience—it can affect your quality of life. Women with AUB may experience:
Recognizing the symptoms early can help in timely diagnosis and treatment. Watch out for the following signs:
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to speak with a gynecologist. At Nelson Hospital, our women’s health specialists can guide you through proper evaluation and care.
It is important to consult with a healthcare provider if you experience any of the following symptoms:
Early treatment and diagnosis can control symptoms and enhance quality of life.
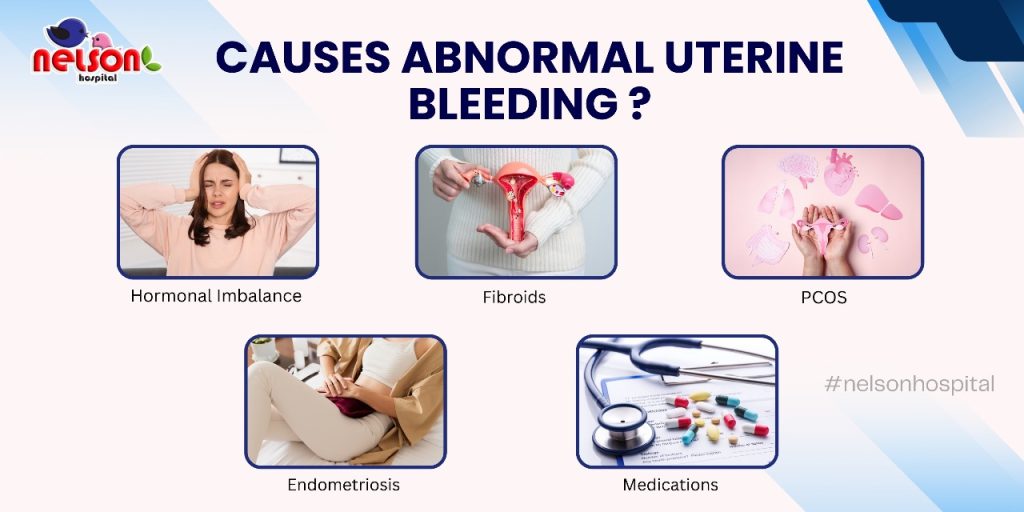
AUB can have several causes. Sometimes, it’s due to a hormonal imbalance. Other times, it may be related to structural problems in the uterus or underlying medical conditions.
1. Hormonal Imbalance
2. Uterine Fibroids or Polyps
3. Endometriosis
4. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
5. Pregnancy-related Issues
6. Medications
7. Cancer or Precancerous Conditions
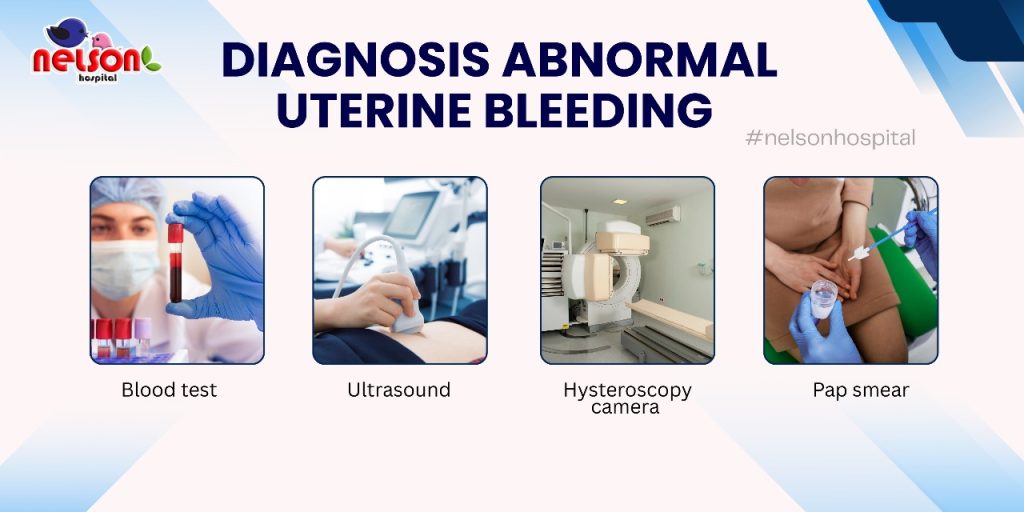
At Nelson Hospital, we follow a step-by-step approach to diagnose AUB:
1. Medical History & Physical Exam
2. Pelvic Examination
3. Blood Tests
4. Ultrasound
5. Pap Smear or Endometrial Biopsy
6. Hysteroscopy
The right treatment depends on the cause, your age, your plans for pregnancy, and overall health. Nelson Hospital offers personalized care with multiple safe and effective options:
1. Lifestyle Changes
2. Medications
3. Intrauterine Device (IUD)
4. Surgical Options (when necessary)
At Nelson Hospital, we focus on minimally invasive procedures whenever possible to reduce recovery time and improve outcomes.
Please do not ignore abnormal bleeding. It can be a sign of something that needs medical attention. See a doctor if you notice:
World Eye Donation Day: Nelson Hospital’s First Eye Implant Surgery…
Why Food Poisoning Is More Common in Monsoon and What…
Why Are Urine Tests Important for Early Disease Detection? When…
Which Food to Avoid for Kidney Stones and What Foods…
When Surgery Is Needed in Urology Cancer Treatment: A Doctor’s…